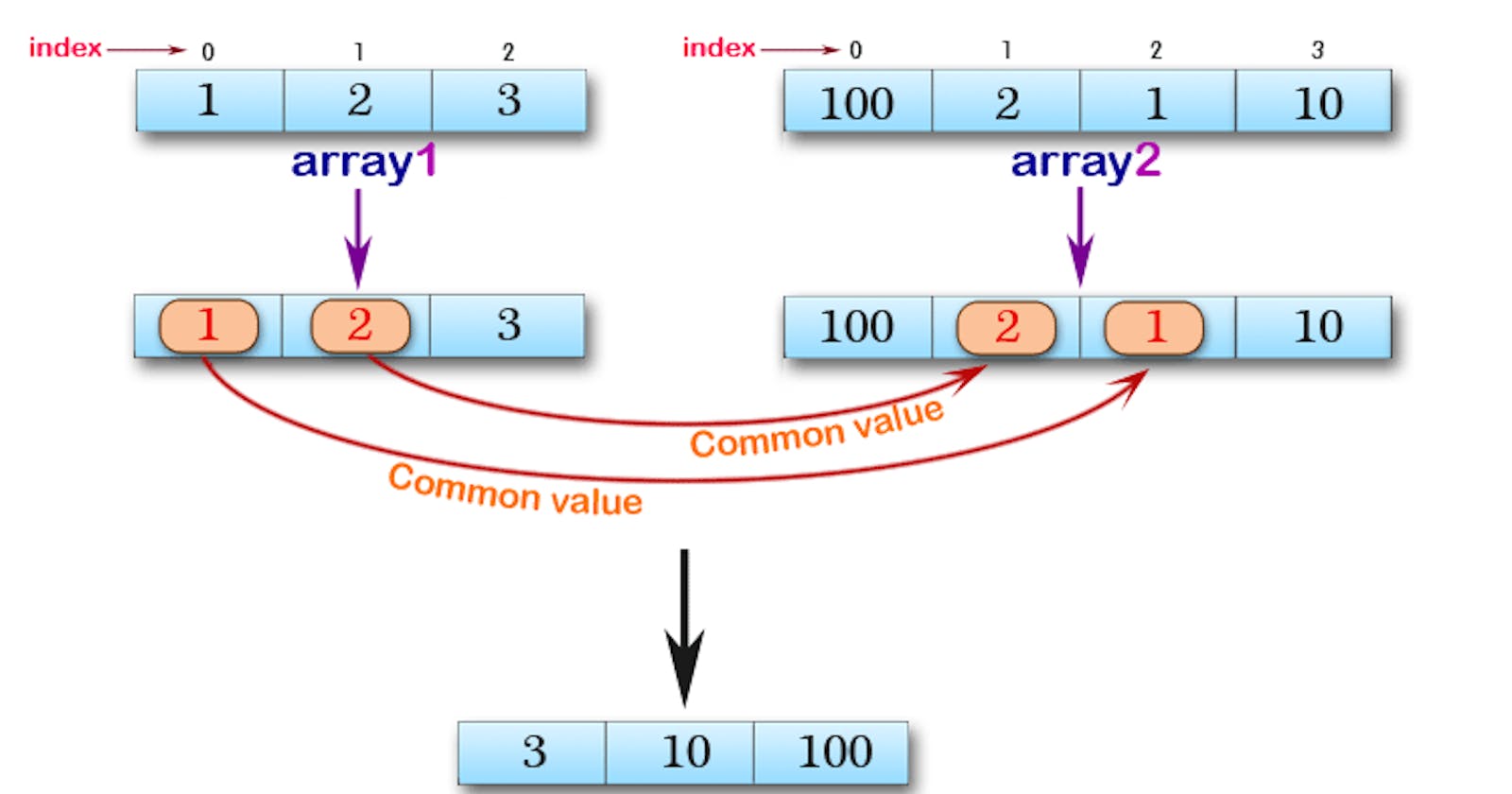
Techniques Used
Approach
- Initialize two hashsets, and add respective elements from both the arrays to their own sets.
- We did the above so that we can easily find the existence of a certain number in each of the sets easily.
- Loop over the
nums1 array elements, if the ith element is contained in s2, then add it to the linkedlist l1.
- Loop over the
nums2 array elements, if the ith element is contained in s1, then add it to the linkedlist l2.
- Add both the linkedlists
l1, and l2 to the resultant list of lists.
Complexity:
- TIme Complexity: O(N + M)
- Space Complexity: O(N + M)
Code: C++
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> findDifference(vector<int>& nums1, vector<int>& nums2) {
unordered_set<int> s1;
unordered_set<int> s2;
for(int i = 0; i < nums1.size(); i++){
s1.insert(nums1[i]);
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums2.size(); i++){
s2.insert(nums2[i]);
}
vector<int> temp;
for(int i: s1){
if(s2.find(i) == s2.end()){
temp.push_back(i);
}
}
vector<vector<int>> res;
res.push_back(temp);
temp.clear();
for(int i: s2){
if(s1.find(i) == s1.end()){
temp.push_back(i);
}
}
res.push_back(temp);
return res;
}
};
Code: Java
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> findDifference(int[] nums1, int[] nums2) {
Set<Integer> s1 = new HashSet<>();
Set<Integer> s2 = new HashSet<>();
fillHashSet(nums1, s1);
fillHashSet(nums2, s2);
List<Integer> l1 = new ArrayList<>();
List<Integer> l2 = new ArrayList<>();
for(int i : nums1){
if(!s2.contains(i)){
if(!l1.contains(i)) l1.add(i);
}
}
for(int i : nums2){
if(!s1.contains(i)){
if(!l2.contains(i)) l2.add(i);
}
}
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
res.add(l1);
res.add(l2);
return res;
}
static void fillHashSet(int[] nums, Set<Integer> set){
for(int i : nums){
set.add(i);
}
}
}